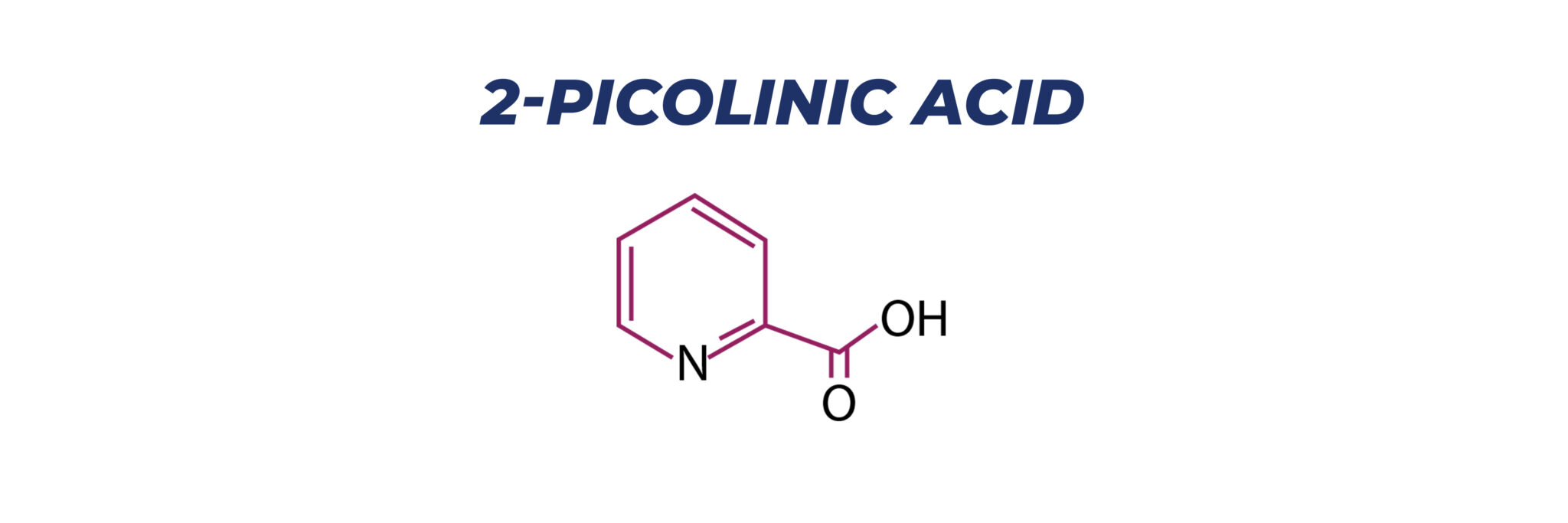
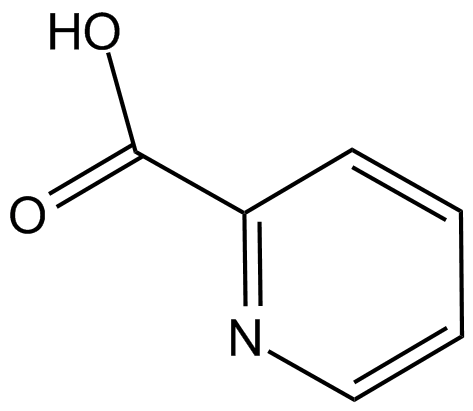
Picolinic acid is an organic compound with the formula NC5H4CO2H. It is a derivative of pyridine with a carboxylic acid (COOH) substituent at the 2-position. It is an isomer of nicotinic acid and isonicotinic acid, which have the carboxyl side chain at the 3- and 4-positions, respectively. It is a white solid although impure samples can appear tan. The compound is soluble in water.
Production
On a commercial scale, picolinic acid is produced by ammoxidation of 2-picoline followed by hydrolysis of the resulting nitrile:
- NC5H4CH3 1.5 O2 NH3 → NC5H4C≡N 3 H2O
- NC5H4C≡N 2 H2O → NC5H4CO2H NH3
It is also produced by oxidation of picoline with nitric acid.
In the laboratory, picolinic acid is formed from 2-methylpyridine by oxidation with potassium permanganate (KMnO4).
Reactions
Hydrogenation of picolinic acid gives piperidine-2-carboxylic acid, a precursor to the drug Mepivacaine.
Picolinic acid is a bidentate chelating agent of elements such as chromium, zinc, manganese, copper, iron, and molybdenum in the human body.
It is a substrate in the Mitsunobu reaction. In the Hammick reaction, picolinic acid reacts with ketones to give pyridine-2-carbonols:
- NC5H4CO2H R2C=O → NC5H4CR2(OH) CO2
Biosynthesis
Picolinic acid is a catabolite of the amino acid tryptophan through the kynurenine pathway. Its function is unclear, but it has been implicated in a variety of neuroprotective, immunological, and anti-proliferative effects. In addition, it is suggested to assist in the absorption of zinc(II) ions and other divalent or trivalent ions through the small intestine.
Picolinates
Salts of picolinic acid (picolinates) include:
- Chromium(III) picolinate
- Zinc picolinate
See also
- Dipicolinic acid
References